 |

A DIALs Server allows remote users to dial in to a LAN and access the resources of the LAN in the same manner as if they were locally attached with a LAN adapter. Similarly, the DIALs Server also allows LAN-attached users to dial out to WAN resources (such as bulletin boards, FAX machines, Internet Service Providers (ISP) and other on-line services) eliminating the need for an analog phone line and modem on their workstation.
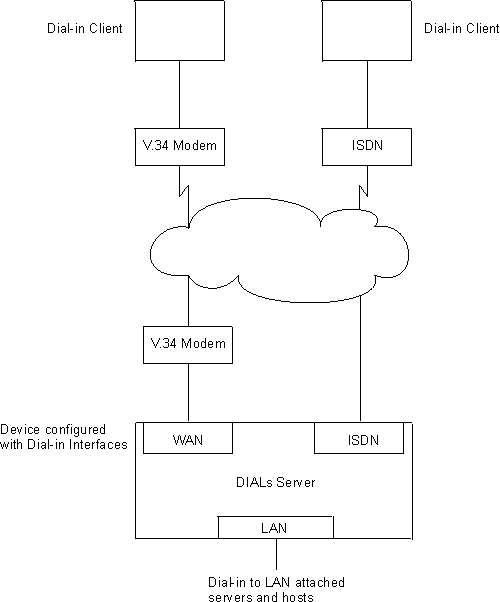
The DIALs Server can be configured for both dial-in and dial-out users simultaneously. The IBM DIALs Dial-In Client runs on the remote workstation and provides the dial-in function. Figure 33 shows an example of a device used as a DIALs Server supporting the dial-in function.
Figure 33. An Example of a DIALs Server Supporting Dial-In

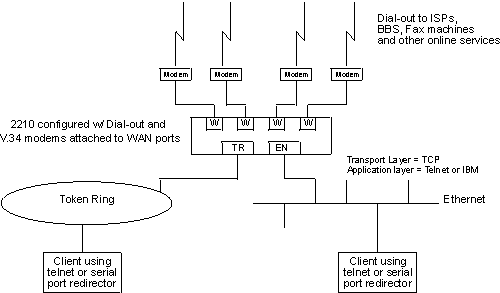
The IBM DIALs Dial-Out Client runs on the network-attached workstation and provides the dial-out function. Figure 34 shows an example of a 2210 used as a DIALs Server supporting the dial-out function.
Figure 34. An Example of a DIALs Server Supporting Dial-Out
Before using Dial-In Access, you need:
This section describes how to configure both dial-in and dial-out functions on the DIALs Server. Configuring a client to use dial-in access is described in the documentation associated with the client the workstation uses.
Dial-in interfaces on the 2210 are a special type of dial-circuit. Because most of the settings for a typical dial-circuit are not relevant for single-user dial-in applications, a new device type called dial-in can be added that sets appropriate defaults for the dial-circuit. Adding a dial-in device also sets up the PPP encapsulator configuration defaults that work with the majority of PPP dial-in clients, including the IBM DIALs Dial-In client. These defaults are described in "Dial Circuit Parameter Defaults for Dial-In Interfaces" and "Dial Circuit PPP Encapsulator Parameters for Dial-In Circuits".
| Note: | DIALs function can only be enabled on dial-in circuits. Dial-in circuits are only supported when the base net is a V.34 or a ISDN net. |
Notes:
The following defaults are set when you add a dial-in interface:
| Note: | "Outbound" for a dial-in circuit is not the same as a dial-out circuit. See "Before Configuring Dial-Out Interfaces". |
| Note: | For a complete description of the following parameters see "Using Point-to-Point Protocol Interfaces" in Software User's Guide. |
The following defaults are set when you add a dial-in interface:
To add a dial-in interface:
Example: Assume the current maximum net is 3 and you want to add 1 dial-in net to the base 2 net.
Figure 35 is an example of defining a dial-in interface.
Figure 35. Adding a Dial-In Interface
Config>add dev dial-in
Adding device as interface 4
Defaulting Data-link protocol to PPP
Use "net 4" command to configure circuit parameters
Base net for this circuit [0]? 2
Enable as a Multilink PPP link? [no]
Disabled as a Multilink PPP link.
Use "set data-link" command to change the data-link protocol
Use "net " command to configure dial circuit parameters.
Config>li dev
Ifc 0 Ethernet CSR 81600, CSR2 80C00, vector 94
Ifc 1 V.34 Base Net CSR 81620, CSR2 80D00, vector 93
Ifc 2 V.34 Base Net CSR 81640, CSR2 80E00, vector 92
Ifc 3 PPP Dial-in Circuit
Ifc 4 PPP Dial-in Circuit
Before configuring and using dial-out interfaces on the 2210, you need:
When using a null modem, use D25NM-3 full handshake:
Pin mapping:
The following steps describe how to configure a dial-out interface on your device.
Notes:
In this environment you can configure the dial-out inactivity timer, the dial-out server name, modem pools, and other parameters.
Modem pools are defined as a group of modems which appear to the user as one modem. When the user needs to dial-out, the first available modem in this pool is used. Modem pools are created in the 2210 DIALs Server by defining groups of dial-out interfaces with the same portname. By default, all dial-out interfaces are named "ALL_PORTS" which creates a modem pool. Naming the dial-out interfaces individually enables a user to select a particular modem to dial-out.
To configure a modem pool:
This section describes the global DIALs Server parameters.
The router can be configured to provide an IP address for a dial-in client to use for the duration of its connection. The address the router will assign to the client can be retrieved by 4 different methods. These methods, in order of priority are listed below:
An IP address can be stored in the PPP user profile for each client. When a client connects and requests an IP address, the router retrieves the address configured in that user's PPP user profile. This allows the user to get the same IP address each time, but requires a unique IP address for every user.
Use the Config> add ppp-user command to configure an IP address in the PPP user profile.
An IP address can be stored in the dial-in interface configuration. When a client connects and request an IP address, the router retrieves the address from the interface through which the connection was made. This method requires a unique IP address for each dial-in interface.
To set the interface IP address:
Blocks of IP addresses can be stored in a IP address pool. When a client connects and requests an address, the router retrieves an address from the pool. When the client disconnects, the address is returned to the pool. This method provides a single location for configuring dial-in client's IP address without the need for an address server.
Use the DIALs config> add ip-pool command to add a pool of IP addresses.
An IP address can be leased from a DHCP server. When a client connects and requests an address, the router requests an address from the DHCP server on behalf of the client. This method requires a DHCP server be present on the LAN or configured in the router. One DHCP server can provide addresses for clients on multiple routers. See Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) for more information.
Use the DIALs config> add dhcp-server command to add a DHCP server.
The IP address used by a dial-in client for the duration of the connection may come from 5 different sources. These sources are listed in order of precedence:
When a dial-in client connects, the router steps through these sources until it finds an address or exhausts all sources. If no IP address can be found, IPCP negotiation fails. Any combination of methods may be used.
The default configuration is:
Client : Enabled UserID : Enabled Interface : Enabled Pool : Enabled DHCP Proxy : Disabled
| Note: | There are no addresses configured by default in the PPP user profile, the interface or the IP address pool. |
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) was developed to provide configuration parameters to hosts on a network. Among other configuration parameters, DHCP has a mechanism for allocation of network addresses to hosts.
The Proxy DHCP feature acts as a client on behalf of a dial-in PPP user. This allows the device to obtain an IP address lease for the duration of the dial-in session, or until the lease expires. The IP address that is allocated from the DHCP server is communicated to the dial-in client through PPP IPCP (see "IP Control Protocol" in the Software User's Guide for a description of IPCP). The dial-in client software has no knowledge that DHCP was used to allocate an IP address, and thus requires no DHCP activation of any kind.
Proxy DHCP requires that at least one DHCP server be configured and accessible from the router.
Proxy DHCP requires that the addresses being allocated to dial-in users be within the same subnet of a directly connected LAN. In a typical configuration, this requires enabling proxy ARP subnet routing to allow the router to answer ARP requests to hosts on the local network on behalf of the dial-in clients.
The most basic configuration calls for a single DHCP server on the same network as the router, with dial-in addresses to be leased within the same subnet as this LAN.
When the client dials in, a lease for an IP address is obtained from the DHCP server and used in IPCP negotiation with the client.
Dials Config>list ip DIALs client IP address specification: Client : disabled UserID : disabled Interface : disabled DHCP Proxy : enabled
Notes:
The configured DHCP server(s) should be IP addresses which are reachable from the connected router. You should always be able to ping the server from the remote access box.
When the DHCP server is located multiple hops away, the server needs to know an address to reply to, and to indicate which pool to allocate an IP address from. The pool to allocate an IP from is important because the DHCP server could be utilized to serve addresses to a number of subnets and there must be some indication as to which pool of addresses to select from. The DHCP Gateway Address (giaddr) is used for this (the terminology is based on the definition given in RFC 2131). The giaddr must be an address that is local to the 2210, such as the token ring or Ethernet LAN port. Also, since the giaddr is the address which the DHCP server will use to reply, make sure you can ping this address from the DHCP server itself.
You can configure multiple DHCP servers for redundancy. When you configure multiple servers, the Proxy DHCP client asks all servers for an address and accepts the first response received. If any of the DHCP servers are more than one hop away, or are connected to a subnet which is not associated with the addresses in its pool, then giaddr must be configured. See "Multiple Hops to DHCP Server".
While there can be more than one DHCP server offering addresses, it is important to not allow the pool of addresses configured at each server to overlap. Further, because there is only one giaddr for the DHCP server to respond to and perform a lookup with, each pool of address must be in the same subnet as each other.
A Domain Name Server (DNS) maps IP addresses to hostnames and is typically static in nature. Dynamic DNS is a feature that, when used with a DDNS DHCP server and a DNS server, enables DHCP to dynamically update the DNS server with an IP address and hostname mapping. This feature may only be used in conjunction with Proxy DHCP.
When you enable Dynamic DNS on the 2210 and you configure a hostname in the user profile (see "PPP Authentication Protocols" in the Software User's Guide), this hostname is passed as option 81 (DDNS) to the DHCP SERVER. If you configured the DHCP server correctly for DDNS, the DHCP server updates the DDNS server with the IP address that it leased to the router and the hostname that the router sent to it. This allows other users to access the dial-in client through the hostname rather than requiring the client to know the dynamically chosen IP address.